- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录2005 > LTC2220IUP-1#TRPBF (Linear Technology)IC ADC 12BIT 185MSPS 64-QFN
20
LTC2220-1
2220_1fa
As with all high speed/high resolution converters, the
digital output loading can affect the performance. The
digital outputs of the LTC2220-1 should drive a minimal
capacitive load to avoid possible interaction between the
digital outputs and sensitive input circuitry. The output
should be buffered with a device such as an ALVCH16373
CMOS latch. For full speed operation the capacitive load
should be kept under 10pF.
Lower OVDD voltages will also help reduce interference
from the digital outputs.
Digital Output Buffers (LVDS Mode)
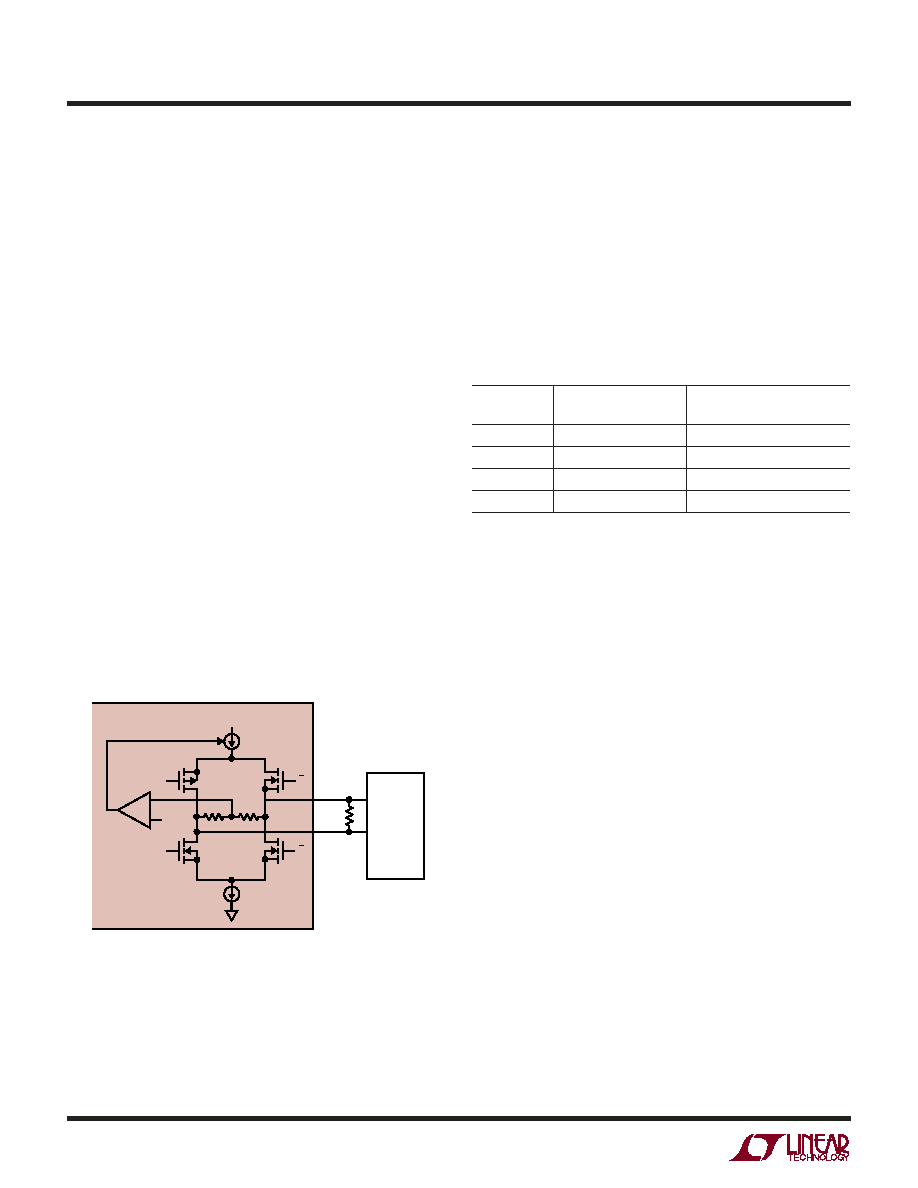
Figure 13b shows an equivalent circuit for a differential
output pair in the LVDS output mode. A 3.5mA current is
steered from OUT+ to OUT– or vice versa which creates a
±350mV differential voltage across the 100 termination
resistor at the LVDS receiver. A feedback loop regulates
the common mode output voltage to 1.25V. For proper
operation each LVDS output pair needs an external 100
termination resistor, even if the signal is not used (such as
OF+/OF– or CLKOUT+/CLKOUT–). To minimize noise the
PC board traces for each LVDS output pair should be
routed close together. To minimize clock skew all LVDS PC
board traces should have about the same length.
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
WU
UU
Table 3. MODE Pin Function
Clock Duty
MODE Pin
Output Format
Cycle Stablizer
0
Offset Binary
Off
1/3VDD
Offset Binary
On
2/3VDD
2’s Complement
On
VDD
2’s Complement
Off
Data Format
The LTC2220-1 parallel digital output can be selected for
offset binary or 2’s complement format. The format is
selected with the MODE pin. Connecting MODE to GND or
1/3VDD selects offset binary output format. Connecting
MODE to 2/3VDD or VDD selects 2’s complement output
format. An external resistor divider can be used to set the
1/3VDD or 2/3VDD logic values. Table 3 shows the logic
states for the MODE pin.
LTC2220-1
22201 F13b
OVDD
LVDS
RECEIVER
OGND
1.25V
D
OUT+
OUT–
100
+
–
3.5mA
10k
Figure 13b. Digital Output in LVDS Mode
Overflow Bit
An overflow output bit indicates when the converter is
overranged or underranged. In CMOS mode, a logic high
on the OFA pin indicates an overflow or underflow on the
A data bus, while a logic high on the OFB pin indicates an
overflow or underflow on the B data bus. In LVDS mode,
a differential logic high on the OF+/OF– pins indicates an
overflow or underflow.
Output Clock
The ADC has a delayed version of the ENC+ input available
as a digital output, CLKOUT. The CLKOUT pin can be used
to synchronize the converter data to the digital system. This
is necessary when using a sinusoidal encode. In all CMOS
modes, A bus data will be updated just after CLKOUTA rises
and can be latched on the falling edge of CLKOUTA. In demux
CMOS mode with interleaved update, B bus data will be
updated just after CLKOUTB rises and can be latched on the
falling edge of CLKOUTB. In demux CMOS mode with si-
multaneous update, B bus data will be updated just after
CLKOUTB falls and can be latched on the rising edge of
CLKOUTB. In LVDS mode, data will be updated just after
CLKOUT+/CLKOUT– rises and can be latched on the falling
edge of CLKOUT+/CLKOUT–.
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
LTC2221IUP#TRPBF
IC ADC 12-BIT 135MSPS 64-QFN
LTC2222IUK-11#TRPBF
IC ADC 11BIT 105MSPS SAMPL 48QFN
LTC2223IUK#TRPBF
IC ADC 12BIT 80MSPS SAMPLE 48QFN
LTC2224IUK#TRPBF
IC ADC 12BIT 135MSPS SAMPL 48QFN
LTC2225IUH#TRPBF
IC ADC 12BIT 10MSPS 3V 32-QFN
LTC2228IUH#TRPBF
IC ADC 12BIT 65MSPS SAMPL 32-QFN
LTC2229IUH#PBF
IC ADC 12-BIT 80MSPS 3V 32-QFN
LTC2231IUP#TRPBF
IC ADC 10BIT 135MSPS 64-QFN
相关代理商/技术参数
LTC2221
制造商:LINER 制造商全称:Linear Technology 功能描述:14-Bit, 80Msps Low Power 3V ADC
LTC2221CUP#PBF
功能描述:IC ADC 12-BIT 135MSPS 64-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 数据采集 - 模数转换器 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 位数:14 采样率(每秒):83k 数据接口:串行,并联 转换器数目:1 功率耗散(最大):95mW 电压电源:双 ± 工作温度:0°C ~ 70°C 安装类型:通孔 封装/外壳:28-DIP(0.600",15.24mm) 供应商设备封装:28-PDIP 包装:管件 输入数目和类型:1 个单端,双极
LTC2221CUP#TRPBF
功能描述:IC ADC 12-BIT 135MSPS 64-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 数据采集 - 模数转换器 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 位数:14 采样率(每秒):83k 数据接口:串行,并联 转换器数目:1 功率耗散(最大):95mW 电压电源:双 ± 工作温度:0°C ~ 70°C 安装类型:通孔 封装/外壳:28-DIP(0.600",15.24mm) 供应商设备封装:28-PDIP 包装:管件 输入数目和类型:1 个单端,双极
LTC2221IUP
制造商:Linear Technology 功能描述:ADC Single Pipelined 135Msps 12-bit Parallel 64-Pin QFN EP
LTC2221IUP#PBF
功能描述:IC ADC 12-BIT 135MSPS 64-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 数据采集 - 模数转换器 系列:- 标准包装:1 系列:- 位数:14 采样率(每秒):83k 数据接口:串行,并联 转换器数目:1 功率耗散(最大):95mW 电压电源:双 ± 工作温度:0°C ~ 70°C 安装类型:通孔 封装/外壳:28-DIP(0.600",15.24mm) 供应商设备封装:28-PDIP 包装:管件 输入数目和类型:1 个单端,双极
LTC2221IUP#TRPBF
功能描述:IC ADC 12-BIT 135MSPS 64-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 数据采集 - 模数转换器 系列:- 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS
Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:2,500 系列:- 位数:12 采样率(每秒):3M 数据接口:- 转换器数目:- 功率耗散(最大):- 电压电源:- 工作温度:- 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:SOT-23-6 供应商设备封装:SOT-23-6 包装:带卷 (TR) 输入数目和类型:-
LTC2222
制造商:LINER 制造商全称:Linear Technology 功能描述:12-Bit,105Msps/80Msps ADCs
LTC2222-11
制造商:LINER 制造商全称:Linear Technology 功能描述:11-Bit, 105Msps ADC